A Guide to SDI Capture for Edge AI
What is SDI Video Capture?
SDI video capture is the process of ingesting uncompressed video signals, transmitted over coaxial cables using the Serial Digital Interface standard, into a computing platform for processing, analysis, or storage. Unlike compressed video formats, SDI delivers broadcast grade quality with near zero latency, making it ideal for real time applications. A capture card or module receives the SDI feed and translates it into a data stream accessible by the host system over PCIe, M.2, or other expansion interfaces. Once ingested, the video can be recorded, streamed, or accelerated through GPU pipelines for advanced workloads such as edge AI inference, defect detection, situational awareness, or autonomous navigation. In industrial edge computing, SDI video capture is the bridge between rugged cameras in the field and the intelligence engines that transform pixels into actionable insight.
As SDI has evolved to deliver higher resolutions and richer detail, its applications have expanded beyond broadcast into diverse edge AI systems where reliable, real time video capture is essential.
Autonomous Vehicles & Drones: Low-latency video feeds from rugged SDI cameras for navigation and object detection.
Industrial Inspection: 4K SDI cameras capture high-resolution imagery for defect detection at production lines.
Defense & Aerospace: Multi-link SDI capture for situational awareness and mission recording.
Medical Imaging : HD-SDI and 3G-SDI for real-time video capture in surgical robots and diagnostic devices.
Broadcast-Grade AI Systems: Edge AI servers using Jetson or x86 capture SDI feeds for live content analysis, streaming, and compliance.
SDI Standards, Resolutions & Configurations
Over the past three decades, SDI has evolved from standard definition broadcast signals into today’s ultra high resolution video transport, advancing in step with the rising demands of industrial computing and AI workloads. Each generation of SD-SDI, HD-SDI, 3G-SDI, 6G-SDI and 12G-SDI has expanded bandwidth to enable higher frame rates, greater color precision, and ever larger pixel counts.
As video resolutions have grown, SDI capture has evolved not only in bitrate but also in how signals are delivered. While single link SDI provides a straightforward path for transmitting standard and high definition video, more demanding formats like 4K and 8K often require dual link or quad link connections to split the data across multiple synchronized channels. These configurations ensure that higher frame rates and larger pixel counts can be transported reliably without compression.
SD-SDI
Bitrate: 270 Mb/s
Resolution Support: 480i (NTSC) or 576i (PAL)
Color Depth: 8–10 bit, uncompressed
Connector Type: BNC coaxial with 75 ohm impedance
Cable Length: Up to 300 meters on high quality coax
Compatibility: Legacy base standard for all subsequent SDI formats
HD-SDI
Bitrate: 1.485 Gb/s
Resolution Support: 720p and 1080i up to 60 Hz
Color Depth: 10 bit, uncompressed
Connector Type: BNC coaxial with 75 ohm impedance
Cable Length: Typically up to 100 meters on quality coax
Compatibility: Backward compatible with SD SDI
3G-SDI
Bitrate: 2.97 Gb/s
Resolution Support: Up to 1080p60
Color Depth: 10 bit, uncompressed
Connector Type: BNC coaxial with 75 ohm impedance
Cable Length: Typically up to 100 meters on quality coax without repeaters
Compatibility: Backward compatible with SD SDI and HD SDI
6G-SDI
Bitrate: 5.94 Gb/s
Resolution Support: Up to 4Kp30 (Ultra HD)
Color Depth: 10 or 12 bit, uncompressed
Connector Type: BNC coaxial with 75 ohm impedance
Cable Length: Typically up to 70 meters on high quality coax
Compatibility: Backward compatible with 3G, HD, and SD SDI
12G-SDI
Bitrate: 11.88 Gb/s
Resolution Support: Up to 4Kp60 (Ultra HD)
Color Depth: 10 or 12 bit, uncompressed
Connector Type: BNC coaxial with 75 ohm impedance (single link)
Cable Length: Typically up to 70 meters on high quality coax
Compatibility: Backward compatible with 6G, 3G, HD, and SD SDI
Dual Link SDI
Two synchronised channels, historically used for 1080p60 before 3G SDI. Still relevant for some high dynamic range workflows.
Quad Link SDI
Four synchronised 3G SDI streams to achieve 4Kp60 before 12G became common. Now applied in some 8K capture setups.
Integrating SDI Frame Grabbers: PCIe, mPCIe & M.2
The edge is not one form factor, it is many. From rugged industrial PCs to compact NVIDIA Jetson systems, SDI capture technology adapts to the architectures shaping the next generation of intelligent computing. Utilising PCIe/mPCIe and M.2 expansion, uncompressed broadcast grade video can flow seamlessly into neural networks at the edge. This flexibility ensures that whether your application is built around a rugged rackmount server or Edge AI gateway, SDI capture is ready to deliver reliable, real time vision.

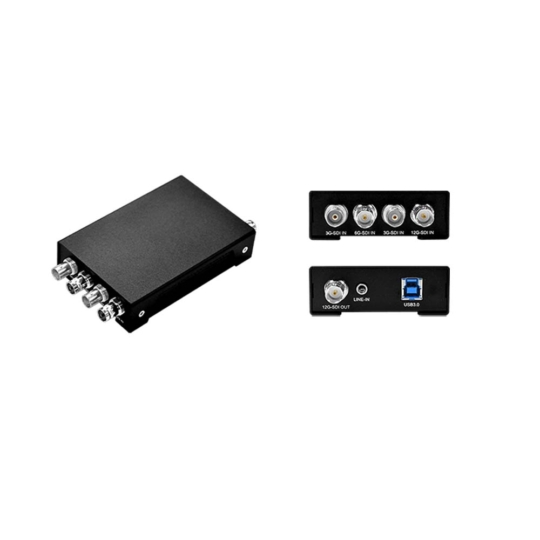
PCIe SDI Capture Cards
Found in rackmount servers, expandable industrial box PCs, and GPU workstations, PCIe capture cards deliver multi channel ingest. Onboard FPGAs or ASICs handle pre-processing tasks such as scaling, color space conversion, and frame synchronization, ensuring host CPUs and GPUs are free for AI inference.
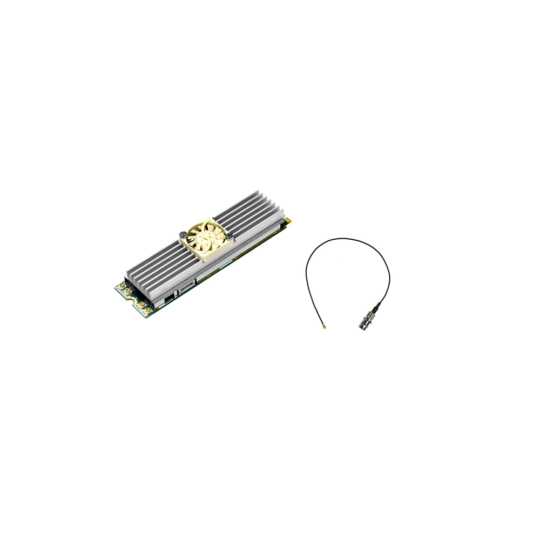
M.2 SDI Capture Cards
Small yet powerful, M.2 SDI capture cards integrate Serial Digital Interface inputs directly into fanless edge devices and embedded platforms. They are increasingly popular in systems built on NVIDIA Jetson and similar edge AI accelerators, where compact size and efficient thermal design are essential.
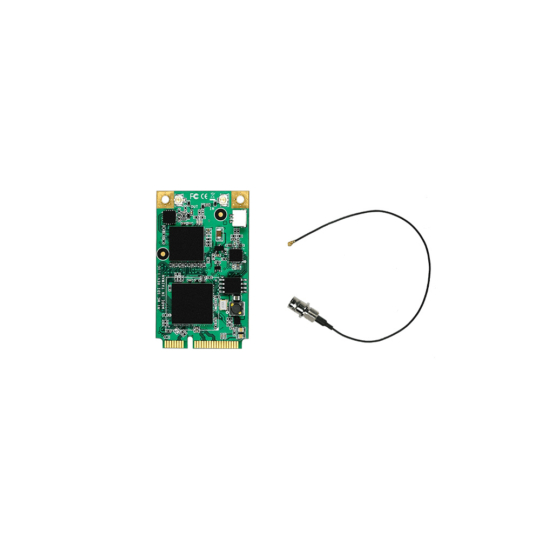
Mini PCIe SDI Capture Cards
Still widely used in rail, aerospace, defense, and medical systems, SDI Mini Card using PCIe signals extend SDI capture into legacy platforms. These ensure long life support in industries where system replacement cycles span decades.

USB SDI Capture Devices
For fast prototyping or portable deployments, USB 3.2 and USB4 SDI capture devices provide plug and play solutions. While not as deterministic as PCIe or M.2, they offer flexibility in environments where expansion slots are limited or field service demands hot swappable devices.
Achieving Low Latency with SDI Capture
In AI workloads, milliseconds matter. Serial Digital Interface video is uncompressed, which means SDI latency is dictated not by transport over the cable but by the capture and processing chain inside the system. Every element of the hardware pipeline, from the capture card to the bus interface to the GPU memory path, determines how quickly pixels become intelligence.
High performance SDI capture devices equipped with FPGAs or ASICs can offload color space conversion, scaling, and synchronization at wire speed, reducing the burden on the host CPU. When paired with later generation PCIe interconnects, these cards deliver the bandwidth required for multi channel 4K or 8K feeds without bottlenecks. M.2 and Mini Card modules extend this capability into compact fanless edge systems, allowing SDI video capture directly at the point of data generation.
With support for GPUDirect RDMA, frames can bypass system memory and stream directly into GPU buffers where CUDA pipelines and TensorRT inference engines execute in real time. This minimizes copy overhead, keeps SDI latency within the sub frame threshold, and enables deterministic response for mission critical systems.
Ready to Deploy SDI Frame Grabbers at the Edge?
We supply SDI capture cards in PCIe, M.2, and Mini Card form factors and integrate them into industrial edge AI systems. Our expertise in GPUDirect and CUDA pipelines helps reduce latency so your applications can see, decide, and act in real time.
