How to Choose the Best Solid State Industrial PC
When choosing an industrial PC for edge computing, understanding the differences between solid-state designs and traditional systems with fans, discrete GPUs, and spinning-disk hard drives is crucial. A solid state industrial PC is built with a fanless chassis which utilises passive cooling, solid-state drives (SSDs), and integrated components, which ultimately makes them more rugged and resistant to environmental challenges such as dust, shock, and vibration. Alongside this, they often feature energy-efficient embedded CPUs and industrial-grade components which support wider operating temperatures. Conversely, an industrial PC built with active cooling systems, discrete GPUs, and spinning-disk hard drives often provide higher performance but are more prone to mechanical failures, require more maintenance, and may struggle in harsh operating conditions.
Key Features to Look for in an Industrial PC with Solid-State Design
Fanless Passive Cooling
Ruggedisation Against Shock & Vibration
Effective Thermal Management
Fanless Industrial PCs and Options for Assisted External Cooling
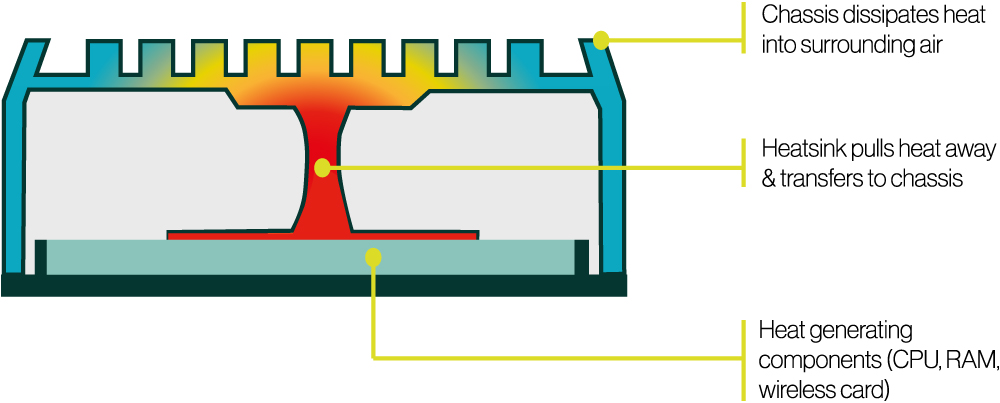
A typical solid state industrial PC utilises natural convection to dissipate heat without relying on fans or active cooling mechanisms. This is achieved by designing the industrial PC’s enclosure to promote efficient heat transfer. Typically, the chassis is constructed from thermally conductive materials, such as aluminium, with external fins or heat sinks to maximise surface area for heat dissipation. As the internal components, like the processor or GPU, generate heat during operation, it is transferred to the chassis through a combination of heat sinks, heat pipes, and thermal pads for mating. The heat is then released into the surrounding air via convection, where warmer air rises and cooler air moves in to replace it, creating a continuous airflow cycle. This design eliminates moving parts, enhancing reliability, reducing noise, and making the solid state industrial PC suitable for environments where dust, vibrations, or maintenance challenges are common.
An illustration of how heat generating components transfer thermal energy across the system chassis to help dissipate heat into the surrounding air.
Passively Cooled Industrial PCs with External Fans
For high-performance edge computing applications, installing an external fan on an industrial PC offers some key advantages, particularly where effective cooling becomes an issue. By actively expelling heat from the system chassis, external fans prevent overheating and allow the industrial PC to maintain optimal performance without thermal throttling, even under heavy computational loads or prolonged use. This improved heat dissipation supports the use of high-performance components, such as powerful processors and GPUs, which generate a significant amount of additional heat. While external fans add mechanical complexity and may require more regular maintenance, their ability to support high-performance computing whilst protecting core internal components, makes them a valuable choice for industrial PCs in demanding applications.
Passively cooled Industrial PC with external fan, preventing dust ingress whilst improving thermal management in a compact footprint.
Solid State Industrial PCs with Conduction Cooling
Another innovative approach utilises conduction cooling by coupling the solid-state industrial PC to a larger, thermally conductive surface for efficient heat dissipation. Replacing conventional heatsink fins with a wide, flat heat spreader allows the industrial PC to interface directly with the surface of a cabinet or enclosure, turning the cabinet into an extended heat-dissipation surface. This helps prevent the internal temperature of the cabinet enclosure increasing and putting additional stress on the industrial PC. Learn more about how our latest industrial PCs with solid-state designs are transforming edge computing in confined, sealed, and waterproof enclosures.
Conduction cooled Industrial PC with flat-top heat spreader designed for coupling with a cabinet enclosure.
Industrial GPU Computers with External PCIe Cassettes
Industrial GPU computers with external PCIe cassettes provide a flexible and powerful solution for Edge AI applications requiring high-performance computing. These systems integrate discrete GPUs into separate ruggedised cassettes, connected to the main industrial PC via a high-speed, cableless PCIe interface. This design improves thermal management by isolating the heat-generating GPU from the primary system and protecting other components from dust ingress. The integration of high-performance GPUs with dampening brackets enables AI inference, deep learning, and real-time data processing in environments subject to continuous shock and vibration, such as onboard vehicles.
Fanless Industrial GPU Computer with external PCIe Cassette for improved thermal management.
Need Help Choosing The Best Solid State Industrial PC?
Tell us about your application and a member of our team will get right back to you.